The Crowns of Florence <
Think of the soldering with which the orb of Santa Maria del Fiore was welded.
Leonardo da Vinci
Paris Ms. G, fol. 84v. Translation: Elizabeth Hughes
In hardly any other European city of the 15th century was the level of literacy as high as in the commercial metropolis of Florence. This meant the wider population could access literature in the Italian vernacular (vernacolo). Literary culture centered around the “Three Crowns of Florence”: Dante Alighieri (1265–1321), Francesco Petrarch (1304–1374), and Giovanni Boccaccio (1313–1375). This triumvirate was naturally represented in Leonardo’s library. For centuries their works set standards for literary style in Italy and beyond and fostered the development of a pre-national Italian identity based on literary language. At the same time, they reflect the encyclopedic horizon of knowledge of the time in which the Christian theological tradition is combined with a secularist worldview. Added to this is the ambition to compete with the ancient models. The openness to new experiences of nature coincides with the striving for a holistic cosmic order increasingly based on scientific knowledge. The visual arts, too, are increasingly characterized by precise observations of nature and detailed depictions, and in their own way seek to fathom the meaning and constitution of the world.
In the extremely versatile workshop of the sculptor, painter, and goldsmith Andrea del Verrocchio (1435–1488), the young Leonardo has the opportunity to acquire practical skills in a wide variety of techniques. At the same time, he internalizes the aesthetic principles of artistic design. From his enthusiastic teacher, who was himself in possession of a respectable library, the ambitious young artist also learns further forms of knowledge, which flow into the conception of the works. These include engineering knowledge and construction principles, theological-philosophical foundations, and classical literary knowledge.
Brunelleschi's Dome <
 | 30.
Florence, 2003 |
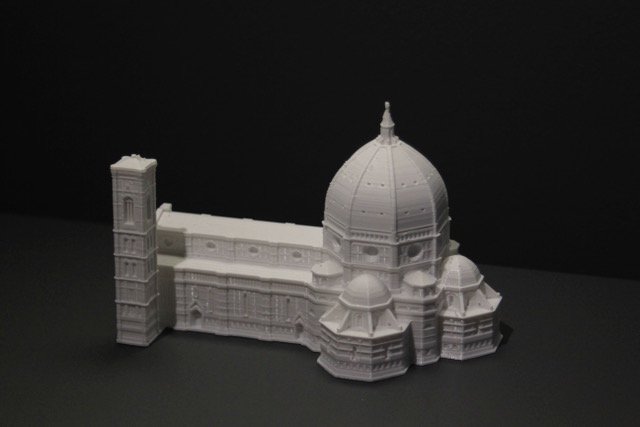

With a span of 41.98 m and a height of 86.79 m above the ground, the octagonal crossing dome of Santa Maria del Fiore dominates the skyline of Florence from far away. The city’s prime landmark with its characteristic steep vaulted dome and the interplay of red-brown brick segments and contrasting white marble ribs is still regarded as the greatest brick dome ever built. It was Filippo Brunelleschi (1377–1446) who mastered the static challenge with a daring rib construction of double-layered brickwork in a herringbone pattern. He managed it without using costly wooden centering and finished the job in record time. Begun in 1420, it was consecrated by Pope Eugen IV on March 25, 1436 (The Day of the Annunciation of the Virgin). But the lantern topped by the gilded copper sphere made by Andrea del Verrocchio was not finally completed until 1471. Verrocchio’s former collaborator Leonardo would still remember it in old age (Paris MS G, fol. 84v).
References
Di Pasquale, Salvatore. 2002. Brunelleschi. La costruzione della cupola di Santa Maria del Fiore. Venice: Marsilio.
Fanelli, Giovanni, and Michele Fanelli. 2004. Die Kuppel Brunelleschis. Geschichte und Zukunft eines großen Bauwerks. Florence: Mandragora.
Haines, Margaret. 2002. “Gli anni della cupola. Archivio digitale delle fonti dell’Opera di Santa Maria del Fiore. Edizione di testi con indici analitici e strutturali.” Reti Medievali Rivista 3 (2): 1–9.
Markschies, Alexander. 2011. Brunelleschi. Munich: C.H. Beck, 45–60.